
The Quran is characterized by a unique phenomenon never found in any other book; 29 suras are prefixed with 14 different sets of “Quranic Initials,” consisting of one to five letters per set. Fourteen letters, half the Arabic alphabet, participate in these initials. The significance of the Quranic initials remained a divinely guarded secret for 14 centuries.
The Quran states in 10:20 and 25:4-6 that its miracle, i.e., proof of divine authorship, was destined to remain secret for a specific predetermined interim:
| They said, “Why hasn’t a miracle come down to him from his Lord?” Say, “Only God knows the future. Therefore, wait, and I will wait along with you.” [10:20] ****** Those who disbelieved said, “This is no more than a fabrication by him, with the help of other people.” Indeed, they uttered a blasphemy; a falsehood. Others said, “Tales from the past that he wrote down; they were dictated to him day and night.” Say, “This was sent down from the One who knows `the secret‘ in the heavens and the earth.” Surely, He is Forgiving, Most Merciful. [25:4-6] |
The Quranic Initials constitute a major portion of the Quran’s 19-based mathematical miracle.
Table 1: List of the Quranic Initials and Their Suras
No. | Sura No. | Sura Title | Quranic Initials |
| 1. | 2 | The Heifer | A.L.M. |
| 2. | 3 | The Amramites | A.L.M. |
| 3. | 7 | The Purgatory | A.L.M.S. |
| 4. | 10 | Jonah | A.L.R. |
| 5. | 11 | Hûd | A.L.R. |
| 6. | 12 | Joseph | A.L.R. |
| 7. | 13 | Thunder | A.L.M.R. |
| 8. | 14 | Abraham | A.L.R. |
| 9. | 15 | Al-Hijr Valley | A.L.R. |
| 10. | 19 | Mary | K.H.Y.‘A.S. |
| 11. | 20 | T.H. | T.H. |
| 12. | 26 | The Poets | T.S.M. |
| 13. | 27 | The Ant | T.S. |
| 14. | 28 | History | T.S.M. |
| 15. | 29 | The Spider | A.L.M. |
| 16. | 30 | The Romans | A.L.M. |
| 17. | 31 | Luqmaan | A.L.M. |
| 18. | 32 | Prostration | A.L.M. |
| 19. | 36 | Y.S. | Y.S. |
| 20. | 38 | S. | S. |
| 21. | 40 | Forgiver | H.M. |
| 22. | 41 | Elucidated | H.M. |
| 23. | 42 | Consultation | H.M. ‘A.S.Q |
| 24. | 43 | Ornaments | H.M. |
| 25. | 44 | Smoke | H.M. |
| 26. | 45 | Kneeling | H.M. |
| 27. | 46 | The Dunes | H.M. |
| 28. | 50 | Q. | Q. |
| 29. | 68 | The Pen | NuN |
Historical Background
In 1968, I realized that the existing English translations of the Quran did not present the truthful message of God’s Final Testament. For example, the two most popular translators, Yusuf Ali and Marmaduke Pickthall, could not overcome their corrupted religious traditions when it came to the Quran’s great criterion in 39:45.
| When God ALONE is mentioned, the hearts of those who do not believe in the Hereafter shrink with aversion. But when others are mentioned beside Him, they rejoice.[39:45] |
Yusuf Ali omitted the crucial word “ALONE” from his translation, and altered the rest of the verse by inserting the word “(gods).” Thus, he utterly destroyed this most important Quranic criterion. He translated 39:45 as follows:
| When God, the One and Only, is mentioned, the hearts of those who believe not in the Hereafter are filled with disgust and horror; but when (gods) other than He are mentioned, behold, they are filled with joy.[39:45] (according to A. Yusuf Ali) |
The expression “When God, the One and Only, is mentioned,” is not the same as saying, “When God alone is mentioned.” One can mention “God, the One and Only,” and also mention Muhammad or Jesus, and no one will be upset. But if “God ALONE is mentioned,” you cannot mention anyone else, and a lot of people — those who idolize Muhammad or Jesus — will be upset. Thus, Yusuf Ali could not bring himself to present the truth of the Quran, if it exposed his corrupted belief.
Marmaduke Pickthall translated “ALONE” correctly, but destroyed the criterion by inserting his personal belief in parentheses; he translated 39:45 as follows:
| And when Allah alone is mentioned, the hearts of those who believe not in the Hereafter are repelled, and when those (whom they worship) beside Him are mentioned, behold! they are glad.[39:45] (according to Marmaduke Pickthal) |
When I saw the truth of God’s word thus distorted, I decided to translate the Quran, at least for the benefit of my own children. Since I was a chemist by profession, and despite my extensive religious background — my father was a renowned Sufi leader in Egypt — I vowed to God that I would not move from one verse to the next unless I fully understood it.
I purchased all the available books of Quranic translations and exegeses (Tafseer) I could find, placed them on a large table, and began my translation. The first sura, The Key, was completed in a few days. The first verse in Sura 2 is “A.L.M.” The translation of this verse took four years, and coincided with the divine unveiling of “the secret,” the great mathematical Miracle of the Quran.
The books of Quranic exegeses unanimously agreed that “no one knows the meaning or significance of the Quranic Initials A.L.M., or any other initials.” I decided to write the Quran into the computer, analyze the whole text, and see if there were any mathematical correlations among these Quranic initials.
I used a time-share terminal, connected by telephone to a giant computer. To test my hypothesis, I decided to look at the single-lettered Quranic Initials — “Q” (Qaaf) of Suras 42 and 50, “S” (Saad) of Suras 7, 19, and 38, and “N” (Noon) of Sura 68. As detailed in my first book MIRACLE OF THE QURAN: SIGNIFICANCE OF THE MYSTERIOUS ALPHABETS (Islamic Productions, 1973), many previous attempts to unravel the mystery had failed.
The Quranic Initial “Q” (Qaaf)
The computer data showed that the text of the only Q-initialed suras, 42 and 50, contained the same number of Q’s, 57 and 57. That was the first hint that a deliberate mathematical system may exist in the Quran.
Sura 50 is entitled “Q,” prefixed with “Q,” and the first verse reads, “Q, and the glorious Quran.” This indicated that “Q” stands for “Quran,” and the total number of Q’s in the two Q-initialed suras represents the Quran’s 114 suras (57+57 = 114 = 19×6). This idea was strengthened by the fact that “the Quran” occurs in the Quran 57 times.
The Quran is described in Sura “Q” as “Majid” (glorious), and the Arabic word “Majid” has a gematrical value of 57: M (40)+J (3)+I (10)+D (4) = 57.
Sura 42 consists of 53 verses, and 42+53 = 95 = 19×5.
Sura 50 consists of 45 verses, and 50+45 = 95, same total as in Sura 42.
By counting the letter “Q” in every “Verse 19” throughout the Quran, the total count comes to 76, 19×4. Here is a summary of the Q-related data:
- The frequency of occurrence of “Q” in Sura “Q” (No. 50) is 57, 19×3.
- The letter “Q” occurs in the other Q-initialed sura (No. 42) exactly the same number of times, 57.
- The total occurrence of the letter “Q” in the two Q-initialed suras is 114, which equals the number of suras in the Quran.
- “The Quran” is mentioned in the Quran 57 times.
- The description of the Quran as “Majid” (Glorious) is correlated with the frequency of occurrence of the letter “Q” in each of the Q-initialed suras. The word “Majid” has a gematrical value of 57.
- Sura 42 consists of 53 verses, and 42+53 is 95, or 19×5.
- Sura 50 consists of 45 verses, and 50+45 is also 95, 19×5.
- The number of Q’s in all verses numbered “19” throughout the Quran is 76, 19×4.
Glimpses of the Quran’s mathematical composition began to emerge. For example, it was observed that the people who disbelieved in Lot are mentioned in 50:13 and occur in the Quran 13 times — 7:80; 11:70, 74, 89; 21:74; 22:43; 26:160; 27:54, 56; 29:28; 38:13; 50:13; and 54:33. Consistently, they are referred to as “Qawm,” with the single exception of the Q-initialed Sura 50 where they are referred to as “Ikhwaan.” Obviously, if the regular, Q-containing word “Qawm” were used, the count of the letter “Q” in Sura 50 would have become 58, and this whole phenomenon would have disappeared. With the recognized absolute accuracy of mathematics, the alteration of a single letter destroys the system.
Another relevant example is the reference to Mecca in 3:96 as “Becca!” This strange spelling of the renowned city has puzzled Islamic scholars for many centuries. Although Mecca is mentioned in the Quran properly spelled in 48:24, the letter “M” is substituted with a “B” in 3:96. It turns out that Sura 3 is an M-initialed sura, and the count of the letter “M” would have deviated from the Quran’s code if “Mecca” was spelled correctly in 3:96.
NuN (Noon)
This initial is unique; it occurs in one sura, 68, and the name of the letter is spelled out as three letters — Noon Wow Noon — in the original text, and is therefore counted as two N’s. The total count of this letter in the N-initialed sura is 133, 19×7.
The fact that “N” is the last Quranic Initial (see Table 1) brings out a number of special observations. For example, the number of verses from the first Quranic Initial (A.L.M. of 2:1) to the last initial (N. of 68:1) is 5263, or 19×277.
The word “God” (Allah) occurs 2641 (19×139) times between the first initial and the last initial. Since the total occurrence of the word “God” is 2698, it follows that its occurrence outside the initials “A.L.M.” of 2:1 on one side, and the initial “N” of 68:1 on the other side, is 57, 19×3. Tables 9 to 18 prove that the initial “NuN” must be spelled out to show two N’s.
S (Saad)
This initial prefixes three suras, 7, 19, and 38, and the total occurrence of the letter “S” (Saad) in these three suras is 152, 19×8 (Table 2). It is noteworthy that in 7:69, the word “Bastatan” is written in some printings with a “Saad,” instead of “Seen.”
Table 2: The Frequency of Occurrence of the Letter “S” in the Saad-initialed Suras
| Sura No. | Frequency of The letter “S” |
| 7 | 97 |
| 19 | 26 |
| 38 | 29 |
| 152 (19×8) |
This is an erroneous distortion that violates the Quran’s code. By looking at the oldest available copy of the Quran, the Tashkent Copy, it was found that the word “Bastatan” is correctly written with a “Seen” (see photocopy below).

Historical Note
The momentous discovery that “19” is the Quran’s common denominator became a reality in January 1974, coinciding with Zul-Hijjah 1393 A.H. The Quran was revealed in 13 B.H. (Before Hijrah). This makes the number of years from the revelation of the Quran to the revelation of its miracle 1393 + 13 = 1406 = 19×74. As noted above, the unveiling of the Miracle took place in January 1974. The correlation between 19×74 lunar years and 1974 solar years could not escape notice. This is especially uncanny in view of the fact that “19” is mentioned in Sura 74.
Y. S. (Ya Seen)
These two letters prefix Sura 36. The letter “Y” occurs in this sura 237 times, while the letter “S” (Seen) occurs 48 times. The total of both letters is 285, 19×15.
It is noteworthy that the letter “Y” is written in the Quran in two forms; one is obvious and the other is subtle. The subtle form of the letter may be confusing to those who are not thoroughly familiar with the Arabic language. A good example is the word “Araany ![]() ” which is mentioned twice in 12:36. The letter “Y” is used twice in this word, the first “Y” is subtle and the second is obvious. Sura 36 does not contain a single “Y” of the subtle type. This is a remarkable phenomenon, and one that does not normally occur in a long sura like Sura 36. In my book QURAN: VISUAL PRESENTATION OF THE MIRACLE (Islamic Productions, 1982) every “Y” and “S” in Sura 36 is marked with a star.
” which is mentioned twice in 12:36. The letter “Y” is used twice in this word, the first “Y” is subtle and the second is obvious. Sura 36 does not contain a single “Y” of the subtle type. This is a remarkable phenomenon, and one that does not normally occur in a long sura like Sura 36. In my book QURAN: VISUAL PRESENTATION OF THE MIRACLE (Islamic Productions, 1982) every “Y” and “S” in Sura 36 is marked with a star.
H.M. (Ha Mim)
Seven suras are prefixed with the letters “H ![]() ” and “M
” and “M ![]() ;” Suras 40 through 46. The total occurrence of these two letters in the seven H.M.-initialed suras is 2147, or 19×113. The detailed data are shown in Table 3.
;” Suras 40 through 46. The total occurrence of these two letters in the seven H.M.-initialed suras is 2147, or 19×113. The detailed data are shown in Table 3.
Naturally, the alteration of a single letter “H” or “M” in any of the seven H.M.-initialed suras would have destroyed this intricate phenomenon.
Table 3: Occurrence of the Letters “H” and “M” in the Seven H.M.-Initialed Suras
| Sura | Frequency of Occurrence | ||
| No. | “H” | “M” | “H+M” |
| 40 | 64 | 380 | 444 |
| 41 | 48 | 276 | 324 |
| 42 | 53 | 300 | 353 |
| 43 | 44 | 324 | 368 |
| 44 | 16 | 150 | 166 |
| 45 | 31 | 200 | 231 |
| 46 | 36 | 225 | 261 |
| 292 | 1855 | 2147 | |
| (19×113) | |||
`A.S.Q. (`Ayn Seen Qaf)
These initials constitute Verse 2 of Sura 42, and the total occurrence of these letters in this sura is 209, or 19×11. The letter “ `A” (`Ayn) occurs 98 times, the letter “S” (Seen) occurs 54 times, and the letter “Q” (Qaf) occurs 57 times.
A.L.M. (Alef Laam Mim)
The letters “A,” “L,” and “M” are the most frequently used letters in the Arabic language, and in the same order as we see in the Quranic Initials — “A,” then “L,” then “M.” These letters prefix six suras — 2, 3, 29, 30, 31, and 32 — and the total occurrence of the three letters in each of the six suras is a multiple of 19 [9899 (19×521), 5662 (19x 298), 1672 (19×88), 1254 (19×66), 817 (19×43), and 570 (19×30), respectively]. Thus, the total occurrence of the three letters in the six suras is 19874 (19x 1046), and the alteration of one of these letters destroys this phenomenon.
Table 4: Occurrence of the Letters “A,” “L,” and “M” in the A.L.M.-Initialed Suras.
| Sura | Frequency of Occurrence | |||
| No. | “A” | “L” | “M” | Total |
| 2 | 4502 | 3202 | 2195 | 9899 (19×521) |
| 3 | 2521 | 1892 | 1249 | 5662 (19×298) |
| 29 | 774 | 554 | 344 | 1672 (19×88) |
| 30 | 544 | 393 | 317 | 1254 (19×66) |
| 31 | 347 | 297 | 173 | 817 (19×43) |
| 32 | 257 | 155 | 158 | 570 (19×30) |
| 8945 | 6493 | 4436 | 19874 (19×1046) | |
A.L.R. (Alef Laam Ra)
These initials are found in Suras 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15. The total occurrences of these letters in these suras are 2489 (19×131), 2489 (19×131), 2375 (19x 125), 1197 (19×63), and 912 (19×48), respectively (Table 5).
Table 5: Occurrence of the Letters “A,” “L,” and “R” in the A.L.R.-Initialed Suras
| Sura | Frequency of Occurrence | |||
| No. | “A” | “L” | “R” | Total |
| 10 | 1319 | 913 | 257 | 2489 (19×131) |
| 11 | 1370 | 794 | 325 | 2489 (19×131) |
| 12 | 1306 | 812 | 257 | 2375 (19×125) |
| 14 | 585 | 452 | 160 | 1197 (19×63) |
| 15 | 493 | 323 | 96 | 912 (19×48) |
| 5073 | 3294 | 1095 | 9462 (19×498) | |
A.L.M.R. (Alef Laam Mim Ra)
These initials prefix one sura, No. 13, and the total frequency of occurrence of the four letters is 1482, or 19×78. The letter “A” occurs 605 times, “L” occurs 480 times, “M” occurs 260 times, and “R” occurs 137 times.
A.L.M.S. (Alef Laam Mim Saad)
Only one sura is prefixed with these initials, Sura 7, and the letter “A” occurs in this sura 2529 times, “L” occurs 1530 times, “M” occurs 1164 times, and “S” (Saad) occurs 97 times. Thus, the total occurrence of the four letters in this sura is 2529+1530+1164+97 = 5320 = 19×280.
An important observation here is the interlocking relationship involving the letter “S” (Saad). This letter occurs also in Suras 19 and 38. While complementing its sister letters in Sura 7 to give a total that is divisible by 19, the frequency of this letter also complements its sister letters in Suras 19 and 38 to give a multiple of 19 (see Page 380).
Additionally, the Quranic Initial “S” (Saad) interacts with the Quranic Initials “K.H.Y. `A.” (Kaaf Ha Ya `Ayn) in Sura 19 to give another total that is also a multiple of 19 (see Page 383). This interlocking relationship — which is not unique to the initial “S” (Saad) — contributes to the intricacy of the Quran’s numerical code.
K.H.Y.`A.S. (Kaaf Ha Ya `Ayn Saad)
This is the longest set of initials, consisting of five letters, and it occurs in one sura, Sura 19. The letter “K” in Sura 19 occurs 137 times, “H” occurs 175 times, “Y” occurs 343 times, “ `A” occurs 117 times, and “S” (Saad) occurs 26 times. Thus, the total occurrence of the five letters is 137+175+343+117+26 = 798 = 19×42.
H., T.H. (Ta Ha), T.S. (Ta Seen), & T.S.M. (Ta Seen Mim)
An intricate interlocking relationship links these overlapping Quranic Initials to produce a total that is also a multiple of 19. The initial “H.” is found in Suras 19 and 20. The initials “T.H.” prefix Sura 20. The initials “T.S.” are found in Sura 27, while the initials “T.S.M.” prefix its surrounding Suras 26 & 28.
It should be noted at this time that the longer, more complex, interlocking and overlapping initials are found in the suras where uncommonly powerful miracles are narrated. For example, the virgin birth of Jesus is given in Sura 19, which is prefixed with the longest set of initials, K.H.Y.`A.S.
The interlocking initials “H.,” “T.H.,” “T.S.,” and “T.S.M.” prefix suras describing the miracles of Moses, Jesus, and the uncommon occurrences surrounding Solomon and his jinns. God thus provides stronger evidence to support stronger miracles. The frequencies of occurrence of these initials are presented in Table 6.
Table 6: Occurrence of the Quranic Initials “H.,” “T.H.,” “T.S.,” and “T.S.M.” in Their Suras
| Sura | Frequency of | |||
| “H” | “T” | “S” | “M” | |
| 19 | 175 | — | — | — |
| 20 | 251 | 28 | — | — |
| 26 | — | 33 | 94 | 484 |
| 27 | — | 27 | 94 | – |
| 28 | — | 19 | 102 | 460 |
| 426 | 107 | 290 | 944 | |
| 426+107+290+944 = 1767 = (19×93) | ||||
What Is A “Gematrical Value”?
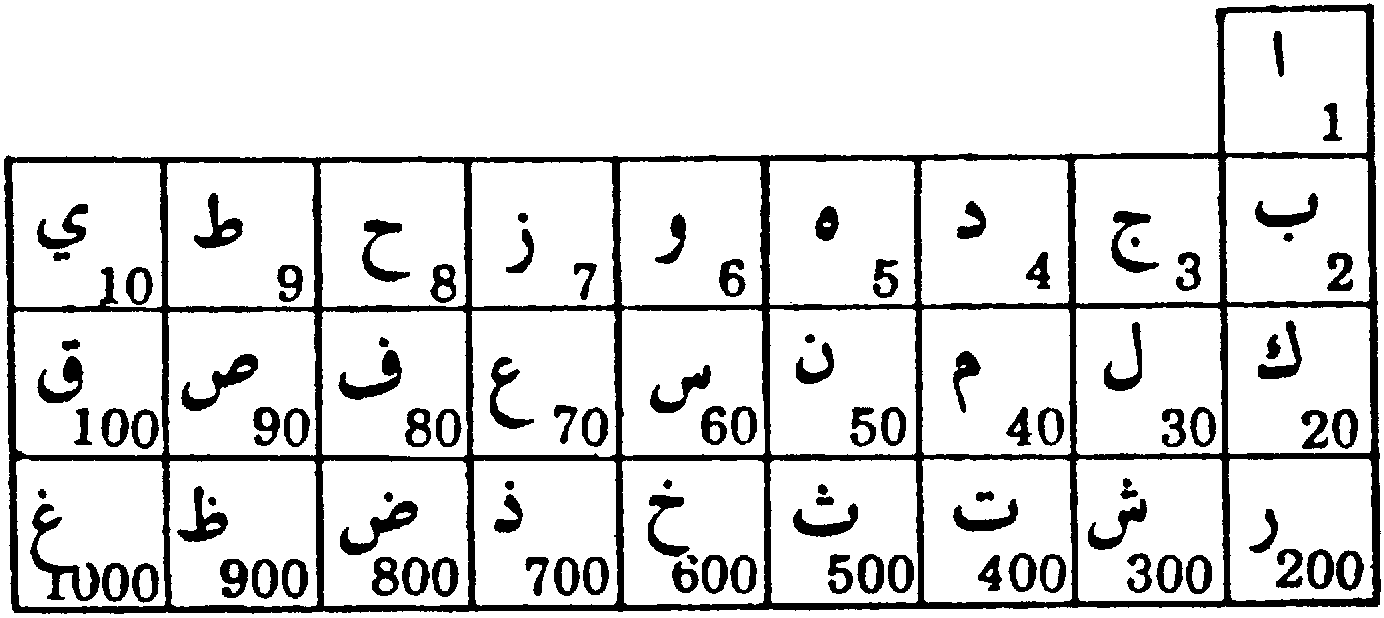
When the Quran was revealed, 14 centuries ago, the numbers known today did not exist. A universal system was used where the letters of the Arabic, Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek alphabets were used as numerals. The number assigned to each letter is its “Gematrical Value.” The numerical values of the Arabic alphabet are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Gematrical Values of the Arabic Alphabet
Other Mathematical Properties of the Initialed Suras
Fourteen Arabic letters, half the Arabic alphabet, participate in the formation of 14 different sets of Quranic Initials. By adding the gematrical value of each one of these letters, plus the number of suras which are prefixed with Quranic Initials (29), we obtain a total of 722, or 19x19x2.
Additionally, if we add the total gematrical value of all 14 initials, plus the number of the first sura where the initial occurs, we get a grand total of 988, 19×52. Table 8 presents these data.
Table 8: The 14 Letters Used in Forming Quranic Initials
| Letter | Value | First Sura |
| A (Alef) | 1 | 2 |
| L (Laam) | 30 | 2 |
| M (Mim) | 40 | 2 |
| S (Saad) | 90 | 7 |
| R (Ra) | 200 | 10 |
| K (Kaf) | 20 | 19 |
| H (Ha) | 5 | 19 |
| Y (Ya) | 10 | 19 |
| `A (`Ayn) | 70 | 19 |
| T (Ta) | 9 | 20 |
| S (Seen) | 60 | 26 |
| H (HHa) | 8 | 40 |
| Q (Qaf) | 100 | 42 |
| N (Noon) | 50 | 68 |
| 693 | 295 | |
| 693 + 295 = 988 = 19×52 | ||
| also 693 + 29 (suras) = 722 = 19x19x2 | ||
If we add the number of occurrences of each of the 14 letters listed in Table 8 as an initial, plus the numbers of the suras where it occurs as an initial, the Grand Total comes to 2033, 19×107. See Table 9.
Table 9: Mathematically Structured Distribution of the Quranic Initials
| Initial | Number of Occurrences | Suras Where It Occurs | Total |
| A (Alef) | 13 | [+ 2 + 3 + 7 + 10 + 11 + 12 + 13 + 14 + 15 + 29 + 30 + 31 + 32] | 222 |
| L (Laam) | 13 | [+ 2 + 3 + 7 + 10 + 11 + 12 + 13 + 14 + 15 + 29 + 30 + 31 + 32] | 222 |
| M (Mim) | 17 | [+ 2 + 3 + 7 + 13 + 26 + 28 + 29 + 30 + 31 + 32 + 40 + 41 + 42 + 43 + 44 + 45 + 46] | 519 |
| S (Saad) | 3 | + 7 + 19 + 38 | 67 |
| R (Ra) | 6 | + 10 + 11 + 12 + 13 + 14 + 15 | 81 |
| K (Kaf) | 1 | + 19 | 20 |
| H (Ha) | 2 | + 19 + 20 | 41 |
| Y (Ya) | 2 | + 19 + 36 | 57 |
| `A (`Ayn) | 2 | + 19 + 42 | 63 |
| T (Ta) | 4 | + 20 + 26 + 27 + 28 | 105 |
| S (Seen) | 5 | + 26 + 27 + 28 + 36 + 42 | 164 |
| H (HHa) | 7 | + 40 + 41 + 42 + 43 + 44 + 45 + 46 | 308 |
| Q (Qaf) | 2 | +42+50 | 94 |
| N (Noon) | 2 | +68 | 70 |
| 79 | 1954 | 2033 | |
| (19×107) |
Table 10 presents the total frequency of Quranic Initials, plus the total gematrical value of these letters in the whole sura. The Grand Total for all initialed suras is 1089479. This number, in excess of one million, is a multiple of 19 (1089479 = 19 x 57341). The slightest alteration or distortion destroys the system.
Note: The total gematrical value of the Quranic Initials in a given sura equals the gematrical value of each initial multiplied by the frequency of occurrence of that initial in the sura.
Major Parameters of the Quranic Initials (Suras, Verses, Frequency, First Sura, & Last Sura)
Table 11 shows that the sum of numbers of suras and verses where the Quranic Initials are found, plus the initial’s frequency of occurrence in that sura, plus the number of the first sura where the initials occur, plus the number of the last sura where the initials occur, produces a total that equals 44232, or 19×2348. Thus, the distribution of the Quranic Initials in the initialed suras is so intricate that their counts and their placement within suras are intertwined to give a grand total that is a multiple of 19.
Table 10: Total Gematrical Values of All Quranic Initials In Their Suras
| Suras | Initials | Frequency of Initials | Total Value in Whole Sura |
| 2 | A.L.M. | 9899 | 188362 |
| 3 | A.L.M. | 5662 | 109241 |
| 7 | A.L.M.S | 5320 | 103719 |
| 10 | A.L.R. | 2489 | 80109 |
| 11 | A.L.R. | 2489 | 90190 |
| 12 | A.L.R. | 2375 | 77066 |
| 13 | A.L.M.R. | 1482 | 52805 |
| 14 | A.L.R. | 1197 | 46145 |
| 15 | A.L.R. | 912 | 29383 |
| 19 | K.H.Y.`A.S. | 798 | 17575 |
| 20 | T.H. | 279 | 1507 |
| 26 | T.S.M. | 611 | 25297 |
| 27 | T.S. | 121 | 5883 |
| 28 | T.S.M. | 581 | 24691 |
| 29 | A.L.M. | 1672 | 31154 |
| 30 | A.L.M. | 1254 | 25014 |
| 31 | A.L.M. | 817 | 16177 |
| 32 | A.L.M. | 570 | 11227 |
| 36 | Y.S. | 285 | 5250 |
| 38 | S. | 29 | 2610 |
| 40 | H.M. | 444 | 15712 |
| 41 | H.M. | 324 | 11424 |
| 42 | H.M.-`A.S.Q. | 562 | 28224 |
| 43 | H.M. | 368 | 13312 |
| 44 | H.M. | 166 | 6128 |
| 45 | H.M. | 231 | 8248 |
| 46 | H.M. | 261 | 9288 |
| 50 | Q | 57 | 5700 |
| 68 | N,N | 133 | 6650 |
| 41388 | 1048091 | ||
| 41388 + 1048091 = 1089479 (19 x 57341) | |||
It is noteworthy that the initial “N” must be counted as two N’s. This reflects the fact that the original Quranic text spells out this initial with 2 N’s.
Table 11: Parameters of the 14 Individual Quranic Initials
| Initial | Sura , Verse, & (Frequency) of Initial in Each Sura | First Sura | Last Sura |
| A (Alef) | 2:1 (4502), 3:1 (2521), 7:1 (2529), 10:1 (1319) 11:1 (1370), 12:1 (1306), 13:1 (605), 14:1 (585), 15:1 (493), 29:1 (774), 30:1 (544), 31:1 (347), 32:1 (257) | 2 | 32 |
| L (Laam) | 2:1 (3202), 3:1 (1892), 7:1 (1530), 10:1 (913), 11:1 (794), 12:1 (812), 13:1 (480), 14:1 (452), 15:1 (323), 29:1 (554), 30:1 (393), 31:1 (297), 32:1 (155) | 2 | 32 |
| M (Mim) | 2:1 (2195), 3:1 (1249), 7:1 (1164), 13:1 (260) 26:1 (484), 28:1 (460), 29:1 (344), 30:1 (317), 31:1 (173), 32:1 (158), 40:1 (380), 41:1 (276), 42:1 (300), 43:1 (324), 44:1 (150), 45:1 (200), 46:1 (225) | 2 | 46 |
| S (Saad) | 7:1 (97), 19:1 (26), 38:1 (29) | 7 | 38 |
| R (Ra) | 10:1 (257), 11:1 (325), 12:1 (257), 13:1 (137), 14:1 (160), 15:1 (96) | 10 | 15 |
| K (Kaf) | 19:1 (137) | 19 | 19 |
| H (Ha) | 19:1 (175), 20:1 (251) | 19 | 20 |
| Y (Ya) | 19:1 (343), 36:1 (237) | 19 | 36 |
| `A (`Ayn) | 19:1 (117), 42:2 (98) | 19 | 42 |
| T (Ta) | 20:1 (28), 26:1 (33), 27:1 (27), 28:1 (19) | 20 | 28 |
| S (Seen) | 26:1 (94), 27:1 (94), 28:1 (102), 36:1 (48), 42:2 (54) | 26 | 42 |
| H (HHa) | 40:1 (64), 41:1 (48), 42:1 (53), 43:1 (44) 44:1 (16), 45:1 (31), 46:1 (36) | 40 | 46 |
| Q (Qaf) | 42:2 (57), 50:1 (57) | 42 | 50 |
| N (NuN) | 68:1 (133) | 68 | 68 |
| 43423 | 295 | 514 | |
| Grand Total = 43423+295+514 = 44232 = 19×2328. | |||
A special mathematical coding authenticates the number of verses where the Quranic Initials themselves are found. As detailed in Table 11, all Quranic Initials occur in Verse 1, except in Sura 42 (initials in Verses 1 and 2). This fact is supported by the remarkable mathematical phenomenon detailed in Table 12. If we multiply the first two columns of Table 12, instead of adding, we still end up with a Total that is divisible by 19 (see Table 13).
Table 12: Mathematical Coding of the Number of Verses with Initials
| Sura No. | No. of Initials | Initialed Verses |
| 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 7 | 4 | 1 |
| 10 | 3 | 1 |
| 11 | 3 | 1 |
| 12 | 3 | 1 |
| 13 | 4 | 1 |
| 14 | 3 | 1 |
| 15 | 3 | 1 |
| 19 | 5 | 1 |
| 20 | 2 | 1 |
| 26 | 3 | 1 |
| 27 | 2 | 1 |
| 28 | 3 | 1 |
| 29 | 3 | 1 |
| 30 | 3 | 1 |
| 31 | 3 | 1 |
| 32 | 3 | 1 |
| 36 | 2 | 1 |
| 38 | 1 | 1 |
| 40 | 2 | 1 |
| 41 | 2 | 1 |
| 42 | 5 | 2 |
| 43 | 2 | 1 |
| 44 | 2 | 1 |
| 45 | 2 | 1 |
| 46 | 2 | 1 |
| 50 | 1 | 1 |
| 68 | 2 | 1 |
| 822 | 79 | 30 |
| 822 + 79 + 30 = 931 (19×49) | ||
Table 13: Multiplying the First Two Columns of Table 12, Instead of Adding
| Sura No. | No. of Initials | Number of Initialed Verses | |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| 3 | 3 | 1 | |
| 7 | 4 | 1 | |
| – | – | – | |
| 42 | 5 | 2 | |
| – | – | – | |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | |
| 68 | 2 | 1 | |
| 2022 | 30 | ||
| 2022 + 30 = 2052 (19×108) | |||
Obviously, it is crucial to have two different initialed verses in Sura 42 in order to conform with the Quran’s mathematical code. The fact that Verse 1 of Sura 42 consists of the two Quranic Initials “H.M.” and the second verse consists of the three Initials “ `A.S.Q.” has perplexed Muslim scholars and orientalists for 14 centuries.
By the end of this Appendix, the reader will see that every element of the Quran is mathematically authenticated. The elements we are dealing with now are “the number of Quranic Initials in each initialed sura” and “the number of verses that contain Quranic Initials.” Tables 11 through 13 have dealt with these two elements.
Additional mathematical authentication is shown in Tables 14 and 15. In Table 14, we have the numbers of all initialed suras added to the number of verses in each sura, plus the number of verses containing initials, plus the gematrical values of those initials. The Grand Total is 7030, or 19×370.
Table 14: Mathematical Properties of the Initialed Suras
| Sura Number | Number of Verses | Number of Initialed Verses | Gematrical Value of the Initials | TOTAL |
| 2 | 286 | 1 | 71 | 360 |
| 3 | 200 | 1 | 71 | 275 |
| 7 | 206 | 1 | 161 | 375 |
| 10 | 109 | 1 | 231 | 351 |
| 11 | 123 | 1 | 231 | 366 |
| 12 | 111 | 1 | 231 | 355 |
| 13 | 43 | 1 | 271 | 328 |
| 14 | 52 | 1 | 231 | 298 |
| 15 | 99 | 1 | 231 | 346 |
| 19 | 98 | 1 | 195 | 313 |
| 20 | 135 | 1 | 14 | 170 |
| 26 | 227 | 1 | 109 | 363 |
| 27 | 93 | 1 | 69 | 190 |
| 28 | 88 | 1 | 109 | 226 |
| 29 | 69 | 1 | 71 | 170 |
| 30 | 60 | 1 | 71 | 162 |
| 31 | 34 | 1 | 71 | 137 |
| 32 | 30 | 1 | 71 | 134 |
| 36 | 83 | 1 | 70 | 190 |
| 38 | 88 | 1 | 90 | 217 |
| 40 | 85 | 1 | 48 | 174 |
| 41 | 54 | 1 | 48 | 144 |
| 42 | 53 | 2 | 278 | 375 |
| 43 | 89 | 1 | 48 | 181 |
| 44 | 59 | 1 | 48 | 152 |
| 45 | 37 | 1 | 48 | 131 |
| 46 | 35 | 1 | 48 | 130 |
| 50 | 45 | 1 | 100 | 196 |
| 68 | 52 | 1 | 50 + 50 | 221 |
| 822 | + 2743 | + 30 | + 3435 | = 7030 (19×370) |
Remarkably, if we multiply the first two columns of Table 14, instead of adding them, we still get a Grand Total that is divisible by 19 (Table 15).
The number of verses per sura, and the numbers assigned to each verse are among the basic elements of the Quran. Not only are these elements authenticated mathematically, but both initialed and un-initialed suras are independently coded. Since we are now dealing with the initialed suras, Table 16 presents the numbers assigned to these suras, added to the numbers of verses in each sura, plus the sum of verse numbers (1+2+3+ … + n). The Grand total is 190133, or 19×10007.
Table 15: Multiplying the First 2 Columns of Table 14, Instead of Adding Them
| Sura Number | Number of Verses | Number of Initialed Verses | Gematrical Value of the Initials | TOTAL | |||||
| 2 | x | 286 | + | 1 | + | 71 | = | 644 | |
| 3 | x | 200 | + | 1 | + | 71 | = | 672 | |
| 7 | x | 206 | + | 1 | + | 161 | = | 1604 | |
| – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| 50 | x | 45 | + | 1 | + | 100 | = | 2351 | |
| 68 | x | 52 | + | 1 | + | (50+50) | = | 3637 | |
| 60071 | 30 | 3435 | = | 63536 (19×3344) | |||||
By adding the number of every sura to the number of the next sura, and accumulating the sums of sura numbers as we continue this process to the end of the Quran, we will have a value that corresponds to each sura. Thus, Sura 1 will have a corresponding value of 1, Sura 2 will have a value of 1+2=3, Sura 3 will have a value of 3+3=6, Sura 4 will have a value of 6+4 = 10, and so on to the end of the Quran. The total values for the initialed and the un-initialed suras are independently divisible by 19. The values for the initialed suras are shown in Table 17.
Table 16: Mathematical Structuring of the Verses of Initialed Suras
| Sura No. | No. of Verses | Sum of Verse #s | Total |
| 2 | 286 | 41041 | 41329 |
| 3 | 200 | 20100 | 20303 |
| 7 | 206 | 21321 | 21534 |
| – | – | – | – |
| 50 | 45 | 1035 | 1130 |
| 68 | 52 | 1378 | 1498 |
| 822 | 2743 | 186568 | 190133 (19×10007) |
Table 17: Values Obtained by Successive Addition of Sura Numbers.
| Sura Number | Calculated Value |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 7 | 28 |
| 10 | 55 |
| 11 | 66 |
| 12 | 78 |
| 13 | 91 |
| 14 | 105 |
| 15 | 120 |
| 19 | 190 |
| 20 | 210 |
| – | – |
| 44 | 990 |
| 45 | 1035 |
| 46 | 1081 |
| 50 | 1275 |
| 68 | 2346 |
| 15675 | |
| (19×825) |
The values calculated for the un-initialed suras add up to a total of 237785, which is also a multiple of 19 (237785 = 19×12515).
Mathematical Coding of Special Words The Word “God” (Allah)
[1] As shown earlier the word “God” occurs in the Quran 2698 times, 19×142.
[2] The numbers of verses where the word “God” occurs add up to 118123, also a multiple of 19 (118123 = 19×6217).
These simple phenomena gave us many difficulties while simply counting the word “God.” We were a group of workers, equipped with computers, and all of us college graduates. Yet, we made several errors in counting, calculating, or simply writing the counts of the word “God.” Those who still claim that Muhammad was the author of the Quran are totally illogical; he never went to college, and he did not have a computer.
[3] From the first Quranic Initials (A.L.M. 2:1) to the last initial (N. 68:1), there are 2641, 19 x 139, occurrences of the word “God.”
[4] The word “God” occurs 57 times in the section outside the Initials (Table 18).
[5] By adding the numbers of the suras and verses where these 57 occurrences of the word “God” are found, we get a total of 2432, or 19×128. See Table 18.
[6] The word “God” occurs in 85 suras. If we add the number of each sura to the number of verses between the first and last occurrences of the word “God,” both verses inclusive, the Grand Total comes to 8170 or 19 x 430. An abbreviated representation of the data is shown in Table 19.
Table 18: Occurrence of the Word “God” outside the Initialed Section
| Number of Sura | Numbers of Verses | Number of Occurrences |
| 1 | 1,2 | 2 |
| 69 | 33 | 1 |
| 70 | 3 | 1 |
| 71 | 3,4,13,15,17,19,25 | 7 |
| 72 | 4,5,7,12,18,19,22,23 | 10 |
| 73 | 20 | 7 |
| 74 | 31,56 | 3 |
| 76 | 6,9,11,30 | 5 |
| 79 | 25 | 1 |
| 81 | 29 | 1 |
| 82 | 19 | 1 |
| 84 | 23 | 1 |
| 85 | 8,9,20 | 3 |
| 87 | 7 | 1 |
| 88 | 24 | 1 |
| 91 | 13 | 2 |
| 95 | 8 | 1 |
| 96 | 14 | 1 |
| 98 | 2,5,8 | 3 |
| 104 | 6 | 1 |
| 110 | 1,2 | 2 |
| 112 | 1,2 | 2 |
| 1798 | 634 | 57 |
| (19×3) | ||
| Sum of numbers of the suras & verses = 1798 + 634 = 2432 | ||
| = 19 x 128 | ||
| Total occurrence of the word “God” outside the initialed section = 57 (19 x 3). | ||
Table 19: All Suras in Which the Word “God” (Allah) Is Mentioned
No | Sura No. | First Verse | Last Verse | # Verses From First to Last |
| 1. | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2. | 2 | 7 | 286 | 280 |
| 3. | 3 | 2 | 200 | 199 |
| – | – | – | – | – |
| 83. | 104 | 6 | – | 1 |
| 84. | 110 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 85. | 112 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3910 | 4260 | |||
| 3910 +4260 =8170 = 19×430 | ||||
| These mathematical properties cover all occurrences of the word “God.” | ||||
[7] The Quran’s dominant message is that there is only “One God.” The word “One,” in Arabic “Wahed” occurs in the Quran 25 times. Six of these occurrences refer to other than God (one kind of food, one door, etc.). The other 19 occurrences refer to God. These data are found in the classic reference INDEX TO THE WORDS OF QURAN.
The crucial importance of the word “ONE” as the Quran’s basic message is manifested in the fact that the Quran’s common denominator, 19, happens to be the gematrical value of the word “ONE.”


